Vulnerability Scanner Software: Best Security Testing Tools
Imagine your digital fortress – your website, your network, your entire online presence – constantly under siege. Silent threats lurk in the shadows, seeking weaknesses to exploit. How do you defend against unseen enemies? The answer lies in proactive vulnerability scanning, a crucial element in today's cybersecurity landscape.
Many organizations struggle to keep pace with the ever-evolving threat landscape. They find themselves burdened by complex configurations, mountains of security alerts, and a nagging fear that something vital is being overlooked. Resource constraints and a lack of specialized expertise often compound these challenges, leaving systems exposed and vulnerable to attack.
This article explores the world of vulnerability scanner software, providing insights into the best security testing tools available to help you fortify your defenses. We'll delve into the features, benefits, and considerations for choosing the right solution for your specific needs, empowering you to proactively identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Choosing the right vulnerability scanner is paramount for maintaining a robust security posture. This guide provides valuable information regarding the best security testing tools, their functionalities, and how they can assist in identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities across your digital infrastructure. By understanding the key aspects of these tools, you can make informed decisions to protect your systems and data from evolving cyber threats. We'll cover various aspects of vulnerability scanning, including different types of scanners, their use cases, and best practices for implementation, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of this critical area of cybersecurity.
The Importance of Automated Vulnerability Scanning
Automated vulnerability scanning is crucial because it provides continuous monitoring and assessment of your systems, something manual processes simply can't match. I remember a past role where we relied heavily on manual penetration testing. While valuable, it was only a snapshot in time. Weeks after a successful pen test, a new vulnerability could emerge, leaving us exposed until the next scheduled assessment. It was a constant game of catch-up, and the pressure to stay ahead of potential threats was immense.
Automated scanners, on the other hand, work tirelessly in the background, identifying vulnerabilities as they arise. They can scan your entire infrastructure – servers, applications, network devices – and provide detailed reports of potential weaknesses. This allows you to prioritize remediation efforts based on the severity of the risk, ensuring that the most critical vulnerabilities are addressed first. Moreover, regular automated scans help maintain compliance with industry regulations and security standards, such as PCI DSS or HIPAA. The ability to demonstrate a consistent security posture is invaluable during audits and assessments, showcasing a commitment to protecting sensitive data and maintaining operational integrity. By integrating automated vulnerability scanning into your security workflow, you can significantly reduce the risk of a successful cyberattack and protect your organization's reputation.
What is a Vulnerability Scanner?
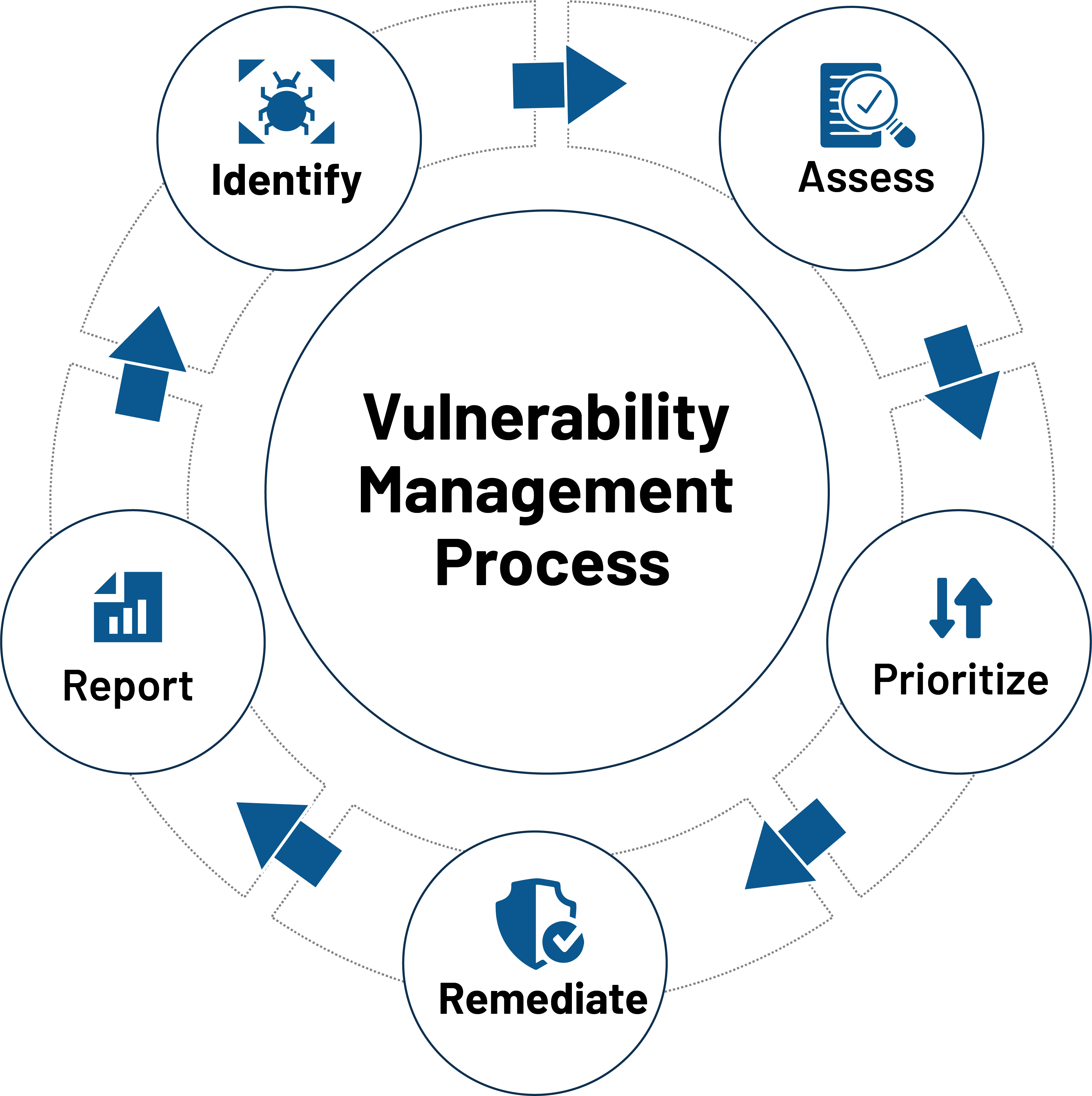
A vulnerability scanner is a software tool designed to identify security weaknesses in computer systems, networks, and applications. Think of it as a digital security guard that tirelessly probes your infrastructure, looking for potential points of entry for malicious actors. These scanners work by comparing the configuration of your systems against a database of known vulnerabilities. If a match is found, the scanner flags the vulnerability, providing details about the potential impact and recommending remediation steps.
Vulnerability scanners come in various forms, including network scanners, web application scanners, and host-based scanners. Network scanners focus on identifying vulnerabilities in network devices, such as routers, switches, and firewalls. Web application scanners specialize in finding weaknesses in web applications, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other common web-based attacks. Host-based scanners, on the other hand, are installed directly on servers or workstations and scan the operating system, applications, and configurations for vulnerabilities. The information gleaned from these scans is used to create actionable remediation plans to bolster security. By regularly using vulnerability scanners, organizations can proactively identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited by attackers.
History and Myths About Vulnerability Scanners
The history of vulnerability scanners dates back to the early days of the internet when security awareness was just beginning to emerge. Early tools were rudimentary, often relying on simple port scanning and banner grabbing to identify potentially vulnerable services. As the threat landscape evolved, so did vulnerability scanners, becoming increasingly sophisticated and capable of detecting a wider range of vulnerabilities. Commercial vulnerability scanners began to appear in the late 1990s and early 2000s, offering organizations more comprehensive and user-friendly solutions for assessing their security posture.
One common myth about vulnerability scanners is that they are a "silver bullet" solution that can completely eliminate security risks. In reality, vulnerability scanners are just one piece of the puzzle. While they are effective at identifying known vulnerabilities, they cannot detect every possible weakness. Organizations still need to implement other security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and security awareness training, to create a layered defense. Another myth is that vulnerability scanners are only useful for large organizations. In fact, businesses of all sizes can benefit from using these tools to proactively identify and address security weaknesses. By dispelling these myths and understanding the true capabilities of vulnerability scanners, organizations can make informed decisions about how to incorporate them into their overall security strategy.
Hidden Secrets of Vulnerability Scanners
One of the hidden secrets of vulnerability scanners lies in their ability to do more than just identify vulnerabilities. Many modern scanners can also prioritize vulnerabilities based on their potential impact and likelihood of exploitation. This allows security teams to focus their remediation efforts on the most critical weaknesses, reducing the risk of a successful attack. Another hidden secret is the importance of properly configuring and tuning vulnerability scanners to match the specific environment in which they are being used.
A poorly configured scanner can generate false positives, leading to wasted time and effort investigating non-existent vulnerabilities. It can also miss real vulnerabilities, leaving systems exposed to attack. To get the most out of a vulnerability scanner, it's essential to understand its capabilities and limitations and to tailor its configuration to the specific needs of your organization. This includes defining scan targets, setting scan schedules, and configuring reporting options. It also involves regularly reviewing scan results and fine-tuning the scanner's configuration to improve its accuracy and efficiency. A final hidden secret is the value of integrating vulnerability scanning with other security tools, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems and vulnerability management platforms. This allows organizations to automate the process of identifying, prioritizing, and remediating vulnerabilities, improving their overall security posture. Unveiling these hidden secrets allows you to maximize the effectiveness of these vital security tools.
Recommendations for Choosing Vulnerability Scanners
When selecting a vulnerability scanner, start by defining your specific needs and requirements. Consider the size and complexity of your infrastructure, the types of applications you need to scan, and your budget. Look for a scanner that offers comprehensive coverage of the vulnerabilities relevant to your environment, including both known and emerging threats.
Evaluate the scanner's accuracy and ability to minimize false positives. A scanner that generates too many false positives can waste valuable time and resources investigating non-existent vulnerabilities. Check for features such as vulnerability prioritization, remediation guidance, and integration with other security tools. Look for a scanner that provides clear and actionable reports, making it easy to identify and address vulnerabilities. Consider the scanner's ease of use and whether it requires specialized expertise to configure and operate. Finally, evaluate the vendor's reputation and track record. Choose a vendor with a proven history of providing reliable and effective vulnerability scanning solutions. Some of the top vulnerability scanners are Nessus, Open VAS, and Qualys.
Specific Vulnerability Scanner Recommendations
Let's delve into some specific vulnerability scanner recommendations, keeping in mind that the best choice for you will depend heavily on your specific needs and environment. Nessus, for instance, is a popular and well-regarded commercial scanner known for its comprehensive vulnerability coverage and ease of use. It offers a wide range of features, including vulnerability scanning, configuration auditing, and malware detection. Nessus is a good choice for organizations of all sizes, but its cost can be a barrier for some smaller businesses. Open VAS, on the other hand, is a free and open-source vulnerability scanner that provides a robust alternative to commercial solutions.
While it may require more technical expertise to configure and operate, Open VAS offers a wealth of features and a large community of users who contribute to its development. Qualys is another leading commercial vulnerability scanner that offers a cloud-based platform for vulnerability management. It provides continuous monitoring and assessment of your systems, allowing you to identify and address vulnerabilities in real-time. Qualys is a good choice for organizations that want a fully managed vulnerability scanning solution. Beyond these three, consider looking at tools like Rapid7's Insight VM, which emphasizes risk-based vulnerability management, or Tenable.io, another cloud-based offering from the makers of Nessus. It's worth trialing a few different scanners in your environment to see which one best fits your workflow and provides the most accurate and actionable results. Remember to factor in not just the initial cost of the scanner, but also the ongoing costs of maintenance, training, and integration with other security tools.
Vulnerability Scanner: Tips for Optimal Use
To get the most out of your vulnerability scanner, it's crucial to develop a well-defined scanning strategy. Start by identifying your critical assets and prioritizing them for scanning. Create a schedule for regular scans, taking into account the frequency of changes to your environment and the severity of potential vulnerabilities. Be mindful of the impact that scanning can have on your systems. Avoid scheduling scans during peak usage hours to minimize performance impact.
Properly configure your scanner to accurately identify vulnerabilities without generating excessive false positives. This may involve tuning the scanner's settings, configuring authentication credentials, and defining scan targets. Integrate your vulnerability scanner with other security tools, such as your SIEM system or vulnerability management platform, to automate the process of identifying, prioritizing, and remediating vulnerabilities. Regularly review scan results and track remediation efforts to ensure that vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner. Finally, stay up-to-date on the latest vulnerabilities and threats and adjust your scanning strategy accordingly. Keep your scanner updated with the latest vulnerability definitions and security patches to ensure that it can accurately identify emerging threats. Regularly review the scanner's configuration and settings to ensure that it is properly configured for your environment.
Understanding Scan Types and Techniques
Understanding the different types of scans and techniques employed by vulnerability scanners is essential for effectively utilizing these tools. Scanners often offer various scan types, such as full scans, quick scans, and targeted scans. Full scans are the most comprehensive, examining all ports and services on a target system. Quick scans focus on commonly used ports and services, providing a faster but less thorough assessment. Targeted scans allow you to focus on specific areas of interest, such as a particular application or service. In addition to scan types, scanners use various techniques to identify vulnerabilities.
These techniques include port scanning, banner grabbing, vulnerability testing, and configuration auditing. Port scanning involves probing a target system to identify open ports, which can indicate running services. Banner grabbing involves retrieving information about the running services, such as the software version. Vulnerability testing involves attempting to exploit known vulnerabilities to confirm their presence. Configuration auditing involves comparing the system's configuration against security best practices. By understanding these different scan types and techniques, you can tailor your scanning strategy to your specific needs and get the most accurate and comprehensive results.
Fun Facts About Vulnerability Scanners
Did you know that the first vulnerability scanner was developed in the late 1980s as a research project? It was a far cry from the sophisticated tools we have today, but it laid the foundation for the vulnerability scanning industry. Another fun fact is that some vulnerability scanners use techniques similar to those used by attackers. They attempt to exploit known vulnerabilities to see if a system is vulnerable, just like a real hacker would. This helps organizations understand their risk and prioritize remediation efforts.
While vulnerability scanners are primarily used for security purposes, they can also be used for other things, such as compliance auditing and network discovery. They can help organizations ensure that their systems are compliant with industry regulations and identify unauthorized devices on their network. The world of vulnerability scanning is constantly evolving, with new techniques and technologies emerging all the time. As attackers develop new ways to exploit systems, vulnerability scanners must adapt and evolve to stay ahead of the curve. This makes vulnerability scanning a challenging but rewarding field, requiring constant learning and innovation. Ultimately, these tools help organizations defend against a wide range of cyber threats.
How to Run a Vulnerability Scan
Running a vulnerability scan typically involves the following steps. First, choose a vulnerability scanner that meets your needs and install it on a system that has network access to the targets you want to scan. Configure the scanner by defining scan targets, setting scan schedules, and configuring authentication credentials. Choose the scan type that best suits your needs. A full scan will provide the most comprehensive results, but it may take longer to complete. A quick scan will be faster, but it may not identify all vulnerabilities.
Start the scan and monitor its progress. The scanner will probe the target systems for vulnerabilities and generate a report of its findings. Review the scan results and prioritize remediation efforts based on the severity of the vulnerabilities. Address the most critical vulnerabilities first, and then work your way down the list. Retest the systems after applying patches or other remediation measures to ensure that the vulnerabilities have been fixed. Regularly repeat the scanning process to identify new vulnerabilities as they emerge. Keep your scanner updated with the latest vulnerability definitions and security patches to ensure that it can accurately identify emerging threats. By following these steps, you can effectively use vulnerability scanners to improve your organization's security posture.
What If a Vulnerability Scan Finds Something?
The discovery of a vulnerability during a scan initiates a critical phase focused on risk management and remediation. Don’t panic! It's far better to find a vulnerability proactively than to have an attacker exploit it. Your immediate response should be to assess the severity of the finding. Most vulnerability scanners provide a risk score or severity rating, which helps you prioritize remediation efforts.
Consider factors such as the potential impact of the vulnerability, the likelihood of exploitation, and the value of the affected assets. Once you have assessed the severity of the vulnerability, develop a remediation plan. This may involve applying security patches, changing configurations, implementing compensating controls, or even decommissioning vulnerable systems. Engage the appropriate teams to implement the remediation plan, such as system administrators, application developers, or network engineers. Track your remediation efforts to ensure that vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner. Retest the systems after applying patches or other remediation measures to confirm that the vulnerabilities have been fixed. Document the entire process, including the vulnerability assessment, remediation plan, and retesting results. This documentation will be valuable for future audits and security assessments. In short, a positive scan result is a call to action, prompting a structured and diligent approach to mitigate risks and strengthen your defenses.
List of Top Vulnerability Scanners
Creating a definitive, static "top" list is challenging because the best scanner depends so much on individual needs. However, some consistently rank high in terms of features, accuracy, and user satisfaction. Here's a list, consider this a starting point for your research:
- Nessus Professional: Widely recognized, extensive vulnerability database.
- Qualys VMDR: Cloud-based, comprehensive vulnerability management.
- Rapid7 Insight VM: Risk-based vulnerability management, integrates with Metasploit.
- Tenable.io: Another cloud-based offering from Tenable, scalable and versatile.
- Open VAS: Free and open-source, powerful but requires technical expertise.
- Acunetix: Web application security scanner, focuses on web vulnerabilities.
- Burp Suite Professional: Another web application security scanner, popular with penetration testers.
- Nikto: Open-source web server scanner, useful for basic web vulnerability checks.
- Nmap: Network mapper, can be used for vulnerability scanning with scripts.
- Tripwire IP360: Enterprise-class vulnerability management, focuses on compliance.
Remember to evaluate each tool based on your specific requirements and conduct trials or proof-of-concepts to determine the best fit.
Question and Answer Section
Here are some common questions about vulnerability scanner software:
Q: How often should I run vulnerability scans?
A: The frequency of scans depends on the criticality of your systems and the rate of change in your environment. Critical systems should be scanned more frequently, ideally weekly or even daily. Less critical systems can be scanned less often, such as monthly or quarterly.
Q: Can vulnerability scanners find all vulnerabilities?
A: No, vulnerability scanners cannot find all vulnerabilities. They are effective at identifying known vulnerabilities, but they may not be able to detect zero-day exploits or custom-developed vulnerabilities. It's important to use vulnerability scanners as part of a layered security approach.
Q: What is the difference between authenticated and unauthenticated scans?
A: Authenticated scans provide the scanner with credentials to log into the target systems. This allows the scanner to access more information and identify more vulnerabilities. Unauthenticated scans do not provide credentials, so they can only identify vulnerabilities that are exposed to the network.
Q: Are vulnerability scanners safe to use?
A: While generally safe, vulnerability scanners can potentially disrupt systems if not configured properly. It's important to run scans during off-peak hours and to avoid scanning critical systems without proper testing. Be sure to consult the scanner's documentation and follow best practices to minimize the risk of disruption.
Conclusion of Vulnerability Scanner Software: Best Security Testing Tools
Vulnerability scanner software is an indispensable component of a robust cybersecurity strategy. These tools enable organizations to proactively identify and address security weaknesses before they can be exploited by attackers. By understanding the different types of scanners, their capabilities, and best practices for implementation, you can make informed decisions to protect your systems and data. Remember to choose a scanner that aligns with your specific needs, regularly update your scanning strategy, and integrate vulnerability scanning with other security tools to create a comprehensive defense. By embracing vulnerability scanning, you can significantly reduce your risk of a successful cyberattack and maintain a strong security posture in today's ever-evolving threat landscape.
Post a Comment