Network Security Software Review: Best Firewall Solutions
In today's digital landscape, the threat of cyberattacks looms large. Imagine your business data, customer information, and financial records held hostage by malicious actors. The thought alone is enough to send shivers down any business owner's spine.
Many businesses struggle with inadequate protection, leading to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Finding the right security solution can feel overwhelming, with a myriad of options promising comprehensive protection but often falling short in practice. It's a challenging landscape to navigate, especially for those without specialized IT expertise.
This review aims to cut through the noise and provide a clear overview of some of the best firewall solutions available. We'll examine features, pricing, and performance to help you make an informed decision about which firewall is right for your organization.
In essence, this article provides a comprehensive analysis of leading firewall solutions. We will explore different types of firewalls, discuss key features to consider, and provide recommendations based on various business needs. Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, understanding your firewall options is crucial for safeguarding your valuable data and maintaining a secure network. We'll cover everything from basic packet filtering to advanced threat intelligence, ensuring you have the knowledge necessary to fortify your defenses against evolving cyber threats. Keywords explored include: firewall solutions, network security, cybersecurity, data protection, threat intelligence, packet filtering.
Understanding Firewall Types
The target here is to help readers understand the varied landscape of firewall technology, allowing them to choose the type best suited for their specific needs. Different firewalls provide different protections.
I remember a time when my own home network was compromised. It was a jarring experience. I had assumed my basic router firewall was sufficient, but I quickly learned that wasn't the case. After that incident, I dove deep into understanding the nuances of firewall technology. It became clear that a one-size-fits-all approach simply doesn't work. Just like different locks offer different levels of security, different firewalls offer different levels of protection. For instance, packet filtering firewalls examine network packets and block or allow them based on pre-defined rules. They're a basic, but essential, first line of defense. Then there are stateful inspection firewalls, which go a step further by tracking the state of network connections. This allows them to identify and block malicious traffic that might appear legitimate on the surface. Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) are the most advanced, incorporating features like intrusion prevention systems (IPS), application control, and deep packet inspection to provide comprehensive security. It's vital to assess your network's specific needs and choose a firewall that aligns with those requirements. A small business might find a stateful inspection firewall sufficient, while a larger enterprise might require the advanced capabilities of an NGFW. The key is to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each type and make an informed decision based on your organization's risk profile and budget. Network security is an investment, and choosing the right firewall is a critical step in protecting your valuable assets. Firewall solutions, network security, and cybersecurity are no longer optional, they are a must.
Key Features to Consider
This section focuses on the essential characteristics that differentiate high-quality firewalls, helping readers evaluate solutions effectively.
What makes a good firewall? It's not just about blocking unwanted traffic; it's about doing it efficiently, intelligently, and with minimal disruption to legitimate business operations. One crucial feature is intrusion prevention system (IPS) capabilities. An IPS actively monitors network traffic for malicious activity and automatically takes steps to block or mitigate threats. Another essential element is application control, which allows you to restrict or allow specific applications from accessing the network. This is particularly important in preventing the spread of malware and controlling employee usage of unauthorized applications. Deep packet inspection (DPI) is also vital. DPI examines the content of network packets to identify and block malicious code or data that might be hidden within legitimate traffic. Reporting and logging capabilities are equally important. A good firewall should provide detailed logs of all network activity, allowing you to identify and investigate security incidents. Finally, ease of management is key. A firewall should be easy to configure and manage, even for users without extensive IT expertise. Consider a user-friendly interface, comprehensive documentation, and readily available support. Features to consider include: intrusion prevention, application control, deep packet inspection, reporting and logging and ease of management. Choosing a firewall with the right features can make the difference between a secure network and a major security breach. Firewall solutions need to consider application control, intrusion prevention, and ease of use.
The Evolution of Firewall Technology: A Brief History
This section aims to contextualize the modern firewall by tracing its development from early packet filters to today's sophisticated NGFWs.
Let's take a trip down memory lane and look at the history of firewalls! The concept of a firewall has evolved significantly over time, from rudimentary packet filters to the sophisticated next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) of today. The first generation of firewalls, developed in the late 1980s, were primarily packet filtering firewalls. These firewalls examined network packets based on source and destination addresses and port numbers, blocking or allowing them based on pre-defined rules. While effective at blocking simple attacks, they were vulnerable to more sophisticated threats. The second generation of firewalls, stateful inspection firewalls, emerged in the early 1990s. These firewalls tracked the state of network connections, allowing them to identify and block malicious traffic that might appear legitimate on the surface. This was a significant improvement over packet filtering firewalls, but they were still limited in their ability to detect and prevent application-layer attacks. The third generation of firewalls, application firewalls, emerged in the late 1990s. These firewalls were able to inspect the content of network traffic and block malicious code or data based on the application being used. This was a major step forward in protecting against application-layer attacks, but they were still limited in their ability to prevent advanced threats. Today, we have next-generation firewalls (NGFWs), which incorporate features like intrusion prevention systems (IPS), application control, and deep packet inspection to provide comprehensive security. NGFWs are the most advanced type of firewall available and are essential for protecting modern networks against evolving cyber threats. Myths surround firewalls - some believe a simple, free firewall is adequate protection, which is often not the case. The history highlights the continuous need to adapt and improve firewall technology to stay ahead of evolving threats. The evolution of the firewall is linked to network security, and cybersecurity practices.
Hidden Secrets of Firewall Configuration
This section explores the often-overlooked aspects of firewall configuration that can significantly impact its effectiveness.
Want to know a secret? A firewall is only as good as its configuration. Many businesses invest in expensive firewalls but fail to properly configure them, leaving them vulnerable to attack. One hidden secret is the importance of regularly reviewing and updating firewall rules. As your network evolves and new applications are added, your firewall rules need to be updated accordingly. Another often-overlooked aspect is the importance of logging and monitoring. A firewall should be configured to log all network activity, and these logs should be regularly reviewed for suspicious activity. This can help you identify and respond to security incidents before they cause significant damage. Furthermore, understanding the default settings and changing them is critical. Many firewalls come with default settings that are not optimized for security. It's essential to review these settings and make sure they are configured appropriately for your specific environment. Another secret is the importance of segmentation. Segmenting your network into different zones and applying different firewall rules to each zone can help limit the impact of a security breach. Finally, consider the principle of least privilege. Only grant users the minimum level of access they need to perform their job duties. This can help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. Properly configuring your firewall is essential for protecting your network against cyber threats. So, dive into the settings, understand the options, and fine-tune your firewall to maximize its effectiveness. This is a critical, yet often overlooked, aspect of network security and firewall solutions. Keywords include firewall configurations, network segmentation, and cybersecurity.
Top Recommended Firewall Solutions for 2024
This section provides specific recommendations for firewall solutions based on different business sizes and needs, offering actionable advice.
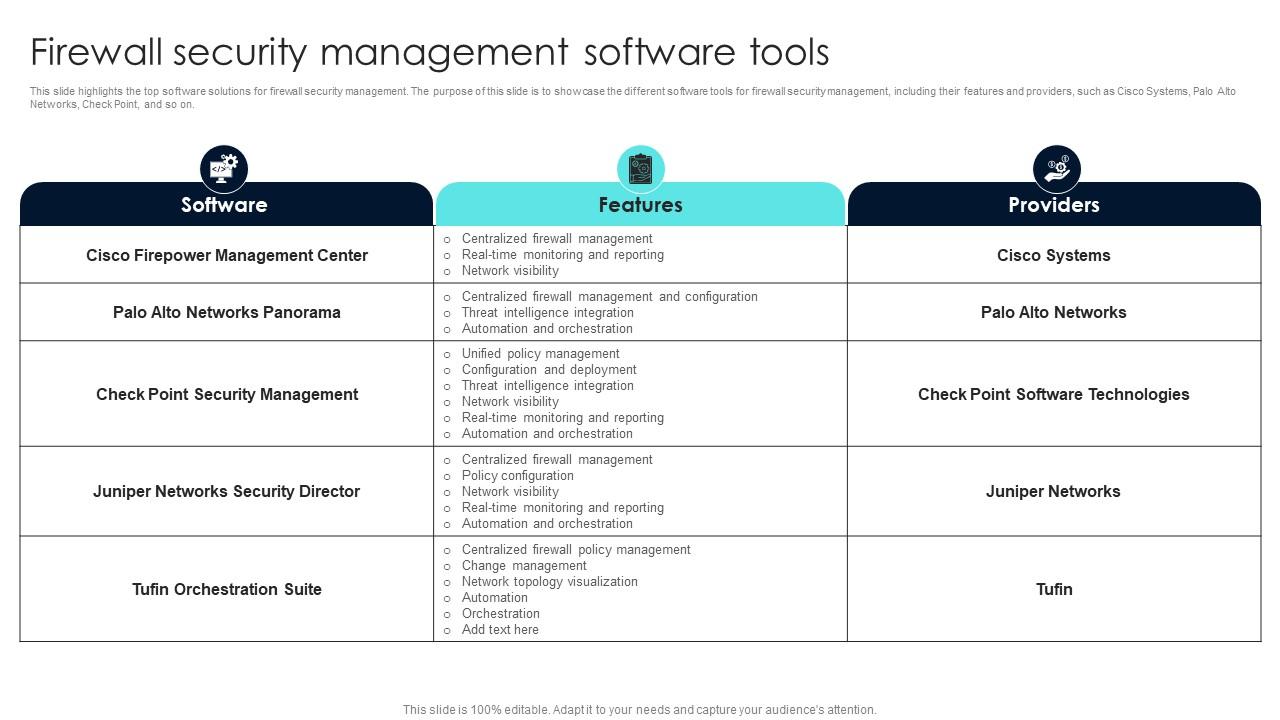
So, which firewall should you choose? It depends on your specific needs and budget. However, here are a few top recommendations for 2024. For small businesses with limited IT expertise, I often recommend a cloud-based firewall solution like Cisco Meraki or Sophos XG Firewall. These solutions are easy to manage and provide comprehensive security features. Cloud-based firewalls offer the benefit of automatic updates and scalability, making them ideal for growing businesses. For mid-sized businesses, I suggest considering a next-generation firewall (NGFW) like Palo Alto Networks or Fortinet. These firewalls offer advanced features like intrusion prevention, application control, and deep packet inspection. They provide a higher level of security and are better equipped to handle sophisticated threats. Large enterprises should consider high-end NGFWs from vendors like Check Point or Juniper Networks. These firewalls offer the highest level of performance and scalability and are designed to protect large, complex networks. Remember to always do your research and compare features and pricing before making a decision. Consider factors like ease of management, reporting capabilities, and customer support. Getting demos and trials can also help you get a feel for the product. Ultimately, the best firewall is the one that meets your specific needs and fits within your budget. Consider cloud-based firewalls, and Next Generation Firewalls. Firewall solutions need to consider business needs and pricing.
Diving Deeper: Understanding Deep Packet Inspection
This section provides a detailed explanation of Deep Packet Inspection, a crucial feature in modern firewalls, explaining its functionality and benefits.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) is a powerful technique used by modern firewalls to examine the content of network packets. Unlike traditional firewalls that only look at the header information of a packet (source and destination addresses, port numbers, etc.), DPI goes deeper and analyzes the actual data being transmitted. This allows firewalls to identify and block malicious code, malware, and other threats that might be hidden within legitimate traffic. DPI works by using a combination of signature-based detection and heuristic analysis. Signature-based detection involves comparing the content of a packet to a database of known malware signatures. If a match is found, the packet is blocked. Heuristic analysis involves looking for suspicious patterns or behaviors in the data. This can help identify new or unknown malware variants that haven't yet been added to the signature database. DPI can also be used for application control. By analyzing the content of packets, firewalls can identify which applications are being used and block or allow them based on pre-defined policies. This can help prevent employees from using unauthorized applications and reduce the risk of malware infections. However, DPI also has some potential drawbacks. It can be resource-intensive, requiring significant processing power to analyze the content of every packet. This can slow down network performance, especially on high-traffic networks. Additionally, DPI can raise privacy concerns, as it involves examining the content of user communications. It's important to implement DPI in a way that respects user privacy and complies with relevant regulations. DPI is essential for modern firewall solutions and network security, but implementation needs to consider the privacy and performance.
Tips for Optimizing Firewall Performance
This section provides actionable tips for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of your firewall, enhancing overall network security.
Optimizing your firewall for peak performance is crucial for maintaining a secure and efficient network. One key tip is to regularly review and update your firewall rules. Over time, your network environment changes, and old rules may become obsolete or even counterproductive. Remove any unnecessary rules and consolidate similar rules to simplify your configuration and improve performance. Another important tip is to enable logging and monitoring. Firewalls generate valuable logs that can help you identify and respond to security incidents. Regularly review these logs for suspicious activity and configure alerts to notify you of potential threats. Caching frequently accessed data can also improve performance. Many firewalls offer caching capabilities that can store frequently accessed data in memory, reducing the need to repeatedly retrieve it from slower storage devices. It’s also important to consider hardware acceleration. Some firewalls offer hardware acceleration features that can offload certain tasks from the CPU, improving performance and reducing latency. Finally, regularly test your firewall to ensure it's working as expected. Use penetration testing tools to simulate real-world attacks and identify any vulnerabilities in your configuration. Following these tips can help you optimize your firewall for peak performance and ensure that your network is protected against evolving cyber threats. Some tips include reviewing rules, enabling logging, and testing the firewall regularly. Firewall solutions must be optimized to consider efficiency.
The Importance of Regular Firewall Audits
This section emphasizes the need for periodic reviews of your firewall configuration and policies to ensure they remain effective and up-to-date.
Regular firewall audits are essential for maintaining a strong security posture. A firewall audit involves a thorough review of your firewall configuration, policies, and logs to identify any weaknesses or vulnerabilities. The frequency of firewall audits depends on the size and complexity of your network, as well as your organization's risk tolerance. However, as a general rule, you should conduct a firewall audit at least once a year, or more frequently if you experience any significant changes to your network environment. During a firewall audit, you should review all of your firewall rules to ensure they are still necessary and effective. Remove any obsolete rules and consolidate similar rules to simplify your configuration. You should also review your logging and monitoring settings to ensure you are capturing the necessary information to detect and respond to security incidents. Additionally, consider penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks and identify any vulnerabilities in your configuration. Penetration testing can help you identify weaknesses in your firewall configuration that might not be apparent during a manual review. Finally, be sure to document all of your firewall audit findings and recommendations. This will help you track your progress and ensure that you are taking the necessary steps to improve your security posture. Regular firewall audits are essential for maintaining a secure network and protecting your organization against evolving cyber threats. This is important for network security, and cybersecurity management in organizations using firewall solutions.
Fun Facts About Firewalls
This section offers some interesting and little-known facts about firewalls, making the topic more engaging and accessible.
Did you know the term "firewall" was originally used in architecture to describe a fire-resistant barrier designed to prevent the spread of fire? It was later adopted by the computer security industry to describe a similar concept – a barrier designed to prevent the spread of malicious software. The first personal firewall software was developed in the early 1990s. It was a simple program that blocked incoming connections to a computer, preventing unauthorized access. The Great Wall of China, one of the most famous structures in the world, shares a conceptual similarity with modern firewalls. Both serve as a defensive barrier against unwanted intrusions. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) often work in conjunction with firewalls. While a firewall blocks unauthorized access, an IDS detects malicious activity that may have bypassed the firewall. Some advanced firewalls use artificial intelligence (AI) to learn and adapt to new threats. AI-powered firewalls can identify and block malicious traffic more effectively than traditional firewalls. The Morris Worm, one of the first major computer security incidents, highlighted the need for firewalls and other security measures. The worm exploited vulnerabilities in Unix systems, causing widespread disruption. The phrase "DMZ" (Demilitarized Zone), often used in networking, also has its origins in military terminology. A DMZ is a network segment that is exposed to the internet but is protected by a firewall. This is a critical step to understand firewall solutions. These facts make network security and cybersecurity practices interesting and accessible. The importance of firewall solutions, network security and cybersecurity.
How to Choose the Right Firewall
This section provides a step-by-step guide on selecting the best firewall solution for your specific needs, simplifying the decision-making process.
Choosing the right firewall can feel overwhelming, but it doesn't have to be. First, assess your network needs. Consider the size of your network, the types of data you store, and your organization's risk tolerance. What are you hoping to protect? This will help you determine the level of security you need. Next, identify your budget. Firewalls range in price from free to thousands of dollars. Determine how much you can afford to spend on a firewall. Third, research different firewall vendors. Read reviews, compare features, and get recommendations from other businesses. Look for a vendor with a good reputation and a track record of providing reliable security solutions. Fourth, consider the features you need. Do you need intrusion prevention, application control, or deep packet inspection? Make a list of the features that are essential for your organization. Fifth, evaluate the ease of management. Choose a firewall that is easy to configure and manage, even for users without extensive IT expertise. Consider a user-friendly interface, comprehensive documentation, and readily available support. Sixth, test the firewall before you buy it. Many vendors offer free trials or demos. Take advantage of these opportunities to test the firewall and make sure it meets your needs. Finally, get professional help if needed. If you're not sure which firewall is right for you, consult with a qualified IT professional. They can assess your network needs and recommend a solution that fits your budget and requirements. These steps include assessing needs, and considering the budget. Choosing the right firewall is important to network security and cybersecurity.
What If My Firewall Fails?
This section addresses the potential consequences of firewall failure and outlines steps to mitigate the impact of such an event.
What happens if your firewall fails? The consequences can be severe. If your firewall fails, your network becomes vulnerable to a wide range of cyber threats, including malware infections, data breaches, and denial-of-service attacks. Your sensitive data could be compromised, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Therefore, it's crucial to have a plan in place to mitigate the impact of a firewall failure. First, have a backup firewall. Consider setting up a secondary firewall that can take over automatically if the primary firewall fails. This can help minimize downtime and maintain a secure network. Second, implement intrusion detection systems (IDS). An IDS can detect malicious activity even if the firewall fails. This can help you identify and respond to security incidents before they cause significant damage. Third, regularly back up your data. If your network is compromised, you can restore your data from a backup. Fourth, have an incident response plan. An incident response plan outlines the steps you will take in the event of a security breach. This can help you respond quickly and effectively to minimize the impact of the incident. Finally, train your employees on security best practices. Employees should be aware of the risks of cyber threats and how to avoid them. This can help prevent human error from leading to security breaches. Preparing for a firewall failure is an essential part of network security and cybersecurity. An incident response plan, and employee training is a must. These are some steps for a firewall solution, network security, and cybersecurity.
Top 5 Common Firewall Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
This section provides a list of common errors in firewall management and offers practical advice on how to prevent them.
Let's discuss the listicle:
1.Default Passwords: One of the most common and easily avoidable mistakes is using default passwords on your firewall. Change the default password immediately to a strong, unique password that is difficult to guess.
2.Outdated Firmware: Running outdated firmware is like leaving the front door of your house unlocked. Regularly update your firewall firmware to patch security vulnerabilities and ensure optimal performance.
3.Permissive Rules: Overly permissive firewall rules can create security holes. Review your rules regularly and restrict access to only what is absolutely necessary. Follow the principle of least privilege.
4.Ignoring Logs: Firewall logs contain valuable information about network activity and potential security threats. Regularly monitor your logs for suspicious activity and investigate any anomalies.
5.Lack of Segmentation: Failing to segment your network into different zones can increase the impact of a security breach. Segment your network and apply different firewall rules to each zone to limit the spread of malware and unauthorized access.
Avoiding these common mistakes can significantly improve your firewall's effectiveness and protect your network from cyber threats. These five tips are essential to network security and cybersecurity. Review the tips to protect your firewall solutions.
Question and Answer
Let's address some questions about the topic.
Q: What is the difference between a hardware firewall and a software firewall?
A: A hardware firewall is a physical appliance that sits between your network and the internet, providing a dedicated layer of security. A software firewall is a program that runs on a computer or server, protecting that specific device. Hardware firewalls typically offer better performance and security than software firewalls.
Q: How often should I update my firewall rules?
A: You should review and update your firewall rules regularly, at least quarterly, or more frequently if you experience any significant changes to your network environment.
Q: What is a next-generation firewall (NGFW)?
A: A next-generation firewall (NGFW) is a type of firewall that incorporates advanced features like intrusion prevention, application control, and deep packet inspection to provide comprehensive security.
Q: Is a firewall enough to protect my network?
A: While a firewall is an essential security tool, it's not enough to protect your network on its own. You should also implement other security measures, such as antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits.
Conclusion of Network Security Software Review: Best Firewall Solutions
In conclusion, selecting and properly configuring a firewall is a cornerstone of robust network security. The landscape of cyber threats is constantly evolving, making it crucial to stay informed and proactive in your security efforts. Whether you choose a cloud-based solution, a hardware appliance, or a next-generation firewall, remember to prioritize features that align with your specific needs, regularly audit your configuration, and stay vigilant in monitoring network activity. By investing in the right firewall and following security best practices, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cyberattacks and protect your valuable data and business operations. Network security, cybersecurity and firewall solutions require regular maintenance, upgrades, and checks.
Post a Comment